The Quantum-Safe Sentinel #4 - January 2026
Welcome to the fourth edition of our Quantum-Safe Sentinel bulletin, and thank you for your continued interest since day one. We wish you all a Quantum-Resilient 2026! 🌟
We said it last month, and we will repeat it all year long: 👉🏽 2026 must be the year of Quantum Cybersecurity Planning. No more delays. Leading CISOs and CIOs who want to be ready on time must start planning their transition now.
Here is what you will find in this month's bulletin:
1️⃣ The quantum cyber threat is closer than ever, and timelines are accelerating. Governments, industry leaders, and standards bodies are converging on concrete implementation schedules. 2026 is the pivotal year for quantum security readiness.
2️⃣ On the Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) front, major technology providers are moving beyond pilots toward default configurations. PQC is now becoming part of baseline infrastructure.
3️⃣ As for Quantum Cryptography, it is always the occasion to take a glimpse at the future. And with the emerging possibility of “Qudits” replacing Qubits, it appears crazier than ever!
➡️ As always, we conclude our newsletter with a focused awareness topic. This month, we address Quantum & Cybersecurity Vocabulary. In this cutting-edge field, even experts sometimes use terms interchangeably, creating unnecessary confusion.
We don’t need more confusion. We need action!
_Mohamed Bassiouny, Quantum Risk and Cybersecurity Lab lead at QuRISK.
1. The Quantum Cyber Threat : Accelerating Timelines
🗞️ Recent News & Trends
The Quantum Insider designated 2026 as the Year of Quantum Security, launching January 12 in Washington D.C. with representatives from the FBI, CISA, and NIST. The year-long global initiative includes regional summits across the Americas, Europe, and Asia-Pacific focused on PQC deployment and quantum IP protection. (Source: The Quantum Insider)
Synergy Quantum released an economic analysis warning that nations face a $12.4 trillion sovereignty crisis as quantum computers approach encryption-breaking capability. The report highlights that cryptographically relevant quantum computers may arrive by 2028, citing IonQ's projections and Google's below-threshold error correction achievement with the Willow chip. (Source: PR Newswire)
Experts from Orange Business and Lastwall predict a sharp increase in quantum-safe security spending in 2026 as PQC migration deadlines become real. U.S. federal agencies face mandates to inventory and replace vulnerable encryption within the decade, while the UK's NCSC and the EU has set a migration target of 2030 (critical data) / 2035 with interim milestones for the next couple of years. (Source: The Quantum Insider)
💡QuRISK's Analyse & Advice
January 2026 marks a watershed moment in quantum threat awareness. Following 2025's designation as the International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, the quantum security conversation has shifted from education to execution. The harvest-now-decrypt-later (HNDL) threat is driving concrete security investments, regulatory mandates, and timeline acceleration across sectors.
The accelerated timeline projections—with some experts now citing 2028 for cryptographically relevant quantum computers—compress the preparation window significantly. Combined with intensifying HNDL campaigns, this creates immediate urgency for organizations handling long-lived sensitive data.
The Year of Quantum Security initiative provides a structured framework for organizations to engage with this transition. Those that treat 2026 as their planning and preparation year will be positioned for systematic implementation; those that delay will face compressed timelines and reactive responses.
2. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) : Becoming Baseline Infrastructure
🗞️ Recent News & Trends
The G7 Cyber Expert Group, co-chaired by the U.S. Department of the Treasury and the Bank of England, released a public statement on January 13, advising financial entities, authorities, and suppliers on key considerations for transitioning to quantum-resilient technology. The statement emphasizes coordinated and timely action, acknowledging that while quantum computers offer significant opportunities, sufficiently mature quantum computers could break widely used cryptographic protocols protecting financial systems and data. (Source : GOV.UK)
As part of Akamai’s phased approach announced in 2025 for PQC adoption, PQC to origin servers using X25519MLKEM768 hybrid key share will become a default feature for all their customers starting January 31, 2026. The company - specialized in content delivery network, cybersecurity, DDoS mitigation, and cloud services - is on track to complete PQC updates across all Akamai-to-Akamai connections by March 2026, enabling full end-to-end quantum-resistant traffic protection. (Source: Akamai)
The U.S. Department of War CIO has secured a five-year agreement with SandboxAQ for Automated Cryptographic Discovery and Inventory (ACDI) using the AQtive Guard platform, establishing a foundation for PQC migration and enhanced cyber readiness. (Source: Quantum Computing Report)
ISACA - an international professional association focused on IT governance - published a comprehensive PQC migration guidance emphasizing a "3Ps" approach (proactive, preventive, and practical strategies). The guidance addresses the reality that cryptography underpins cybersecurity but is often underestimated in its critical role. (Source: ISACA Journal)
💡 QuRISK's Analyse & Advice
The G7 roadmap joins a growing list of coordinated initiatives, including the EU's coordinated roadmap, the UK NCSC's three-phase migration timeline, and U.S. federal mandates, all converging on the same message: the time for action is now.
When major governmental and financial authorities jointly arrive at the same urgency, it really highlights the importance of PQC transition.
With Akamai and other providers moving PQC to default configurations, and Cryptographic Bills of Materials (CBOM) becoming procurement requirements, the market is forcing readiness even where regulation hasn't yet arrived. Organizations must move beyond assessment to implementation: build cryptographic inventories, establish crypto-agility, and begin systematic migration. Waiting is no longer a neutral position, it's falling behind.
3. Quantum Cryptography : Constant Innovation
🗞️ Recent News & Trends
Researchers published breakthrough work on quantum structured light in Nature Photonics, demonstrating methods to engineer light in multidimensional ways that dramatically increase information capacity per photon. This technology shows potential for more secure quantum communication using High Dimensional Quantum Key Distribution (HD QKD) relying on “qudits” (with more than 2 dimensions) instead of qubits. (Source: ScienceDaily)
KAIST and POSTECH researchers developed a 3D printing technique for vertical perovskite nanolasers, offering new pathways for quantum security applications. This technology offers a simpler, more flexible route for developing microphotonic circuitries than can be used for secure quantum interconnects.(Source: Quantum Computing Report)
nodeQ introduced telaQ as a digital twin platform for quantum and quantum-safe network planning, enabling telecommunications operators and enterprises to design next-generation communications infrastructure. The platform distinguishes itself from traditional network observability tools and cryptographic inventory tools by offering pre-deployment scenario analysis and network emulation capabilities, allowing operators to predict how quantum technologies will perform at scale before actual deployment. (Source: PR Newswire)
💡 QuRISK's Analyse & Advice
Quantum cryptography continues advancing toward practical deployment, with January 2026 bringing significant progress in both photonic integration and network infrastructure. While most governments recommend PQC as the primary defense, quantum communication technologies are finding specific applications in high-security corridors and space-based initiatives.
For most organizations, QKD represents a specialized solution for specific high-security applications rather than a universal requirement for everyone. The focus should remain on PQC migration as the foundation, with quantum cryptography considered for use cases requiring physics-based key distribution security. The emergence of planning tools like telaQ's digital twin platform indicates the technology is maturing toward systematic deployment for those with specific requirements.
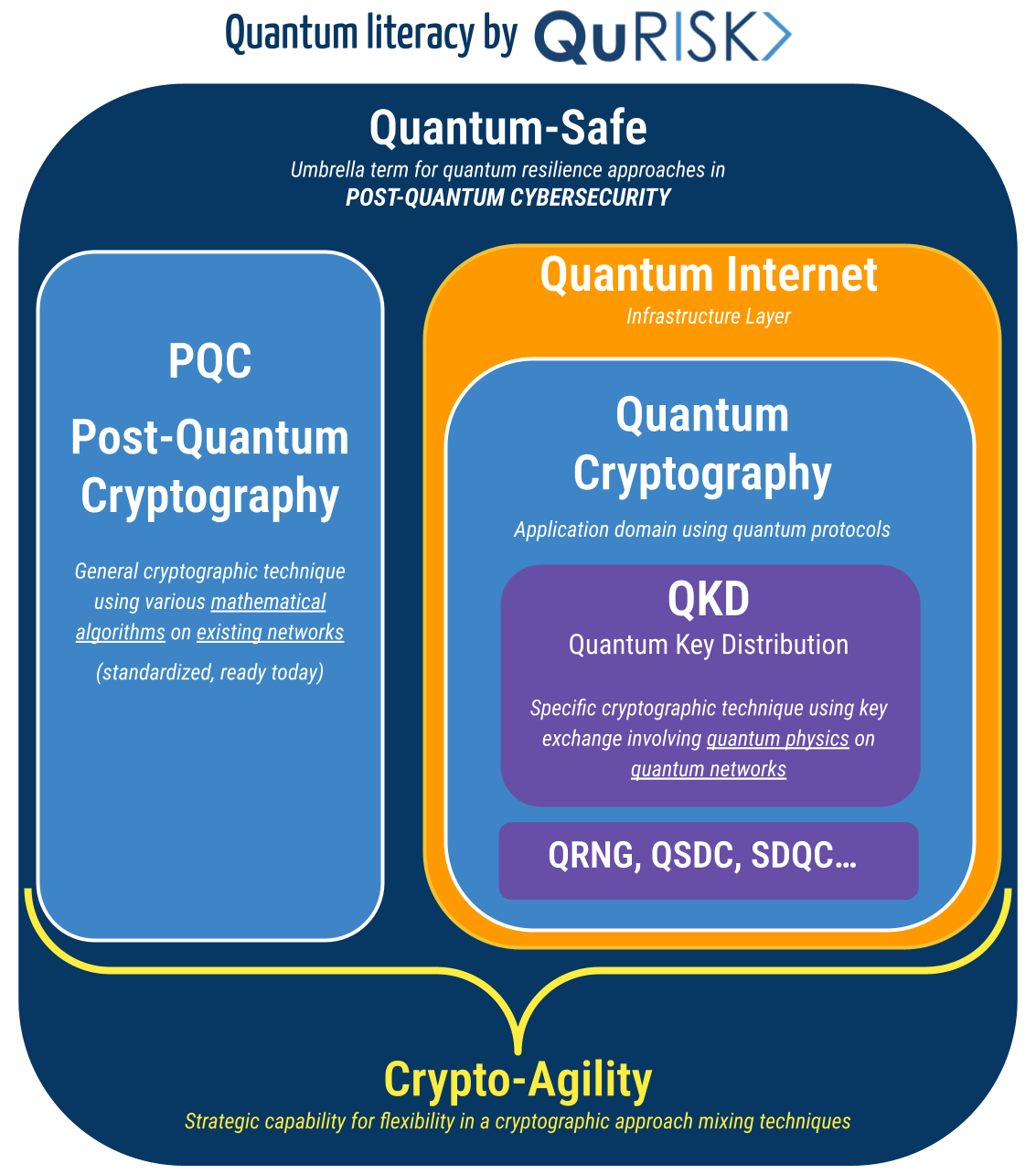
This Month's Awareness Topic: Quantum & Cybersecurity Vocabulary
2026 already shows a coordinated global effort to drive quantum-safe readiness from discussion to implementation. As this trend accelerates, clear terminology becomes essential. Yet concepts such as "post-quantum cybersecurity”, "quantum-safe”, or "quantum cryptography” are often wrongly used, leading to confusion. This month's focus aims to demystify the key terms that are frequently mixed, or misunderstood.
🎓 4 KEY TERMINOLOGIES EXPLAINED
1. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
PQC encompasses classical (= non-quantum) cryptographic algorithms designed to resist attacks from both classical and quantum computers. Examples include CRYSTALS-Kyber and CRYSTALS-Dilithium, which are designed to replace today’s vulnerable public-key schemes such as RSA and elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC). PQC does not require quantum hardware, it runs on today’s systems.
2. Post-Quantum Cybersecurity
It is the broader discipline of preparing cybersecurity practices, architectures, and governance for a world where quantum computers can break existing cryptography. PQC is one component of post-quantum cybersecurity, but it also covers risk assessments, crypto-agility, lifecycle governance, and long-term resilience. Post-Quantum Cybersecurity aims at achieving Quantum-Safety.
3. Quantum-Safe (or Quantum-Resilient)
It is an umbrella term describing any technology, architecture, practice, or strategy designed to remain secure in the presence of quantum threats. Quantum-safe security typically combines: PQC algorithms, strong cryptographic governance, crypto-agility, quantum cryptography where relevant (e.g., QKD or QRNG),long-term resilience planning. Quantum-safe is generally not limited to “quantum cryptography” only, or “PQC” only. It describes the final objective: security that endures in a quantum era by mixing different approaches.
4. Quantum Cryptography
It refers to a family of cryptographic techniques relying on the laws of quantum physics, not mathematical hardness. It includes: Quantum Key Distribution (QKD), Quantum Random Number Generation (QRNG), Quantum Secure Direct Communication (QSDC), Secure Delegated Quantum Computing (SDQC). Quantum cryptography requires quantum hardware and communication infrastructure.
👉🏽 For more explanations, check out our Guide to Quantum Security Concepts.
⭐️ BEST PRACTICES
✅ Promote shared terminology across teams, ensuring quantum, cybersecurity, and IT professionals rely on a synchronized and consistent glossary.
✅ Integrate terminology into cybersecurity awareness programs, so all stakeholders understand the distinctions between PQC, QKD, quantum-safe, and related concepts.
✅ Establish Quantum-Safe awareness programs that explicitly cover these terms and reinforce the differences between cryptographic, quantum, and hybrid approaches.
✅ Include precise terminology in RFPs, policies, architecture documents, and quantum-safe migration plans, to avoid ambiguity during procurement, design, or implementation.
✅ Challenge vendors claims when terminology appears vague, inflated, or misaligned with recognized standards, ensuring expectations match actual capabilities.
🚨 The Quantum-Safe Sentinel is watching for you, helping you stay secure and a step ahead in the Quantum era.
If you appreciate our work for the community, please like and share our publications, follow our page, and promote it to colleagues who may benefit from these insights.
☎️ If you have any suggestions or comments about our publications, or if you would like to discuss these important topics with one of our experts, feel free to book a meeting at www.qurisk.fr or to contact us contact@qurisk.fr.
🙌🏼 Stay tuned for more to come. Stay healthy, and quantum-safe to you all.
🦉 This bulletin is powered by oQo, QuRISK’s Quantum Virtual Advisor: an AI-driven LLM designed to augment professionals on quantum technology–related themes, including securing adoption, risk management, and cybersecurity. To learn more about oQo, please visit www.myoqo.ai.
It is published by QuRISK - Quantum Risk Advisory, a French firm specialized in Quantum Risk & Cybersecurity.